How to Use a PH Tester for Accurate Soil and Water Testing
Understanding the pH levels in soil and water is crucial for gardening, farming, and environmental monitoring. A pH tester is an invaluable tool that allows users to measure the acidity or alkalinity of these elements, ensuring that they provide optimal growing conditions for plants and accurate readings for various water applications. In this guide, we will explore the importance of pH testing, how the pH tester works, and practical steps for obtaining precise measurements.
With the increasing emphasis on sustainable practices and environmental health, knowing how to utilize a pH tester is more essential than ever. By regularly monitoring pH levels, individuals can make informed decisions that enhance soil fertility, improve plant health, and protect water quality. This knowledge not only benefits personal gardening and horticulture efforts but is also vital for agricultural productivity and ecological conservation.
In the following sections, we will delve into the step-by-step process of using a pH tester effectively, highlighting tips for getting accurate results and maintaining the instrument for long-term use. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or a beginner, mastering pH testing will equip you with the information needed to foster thriving plants and maintain healthy water systems.
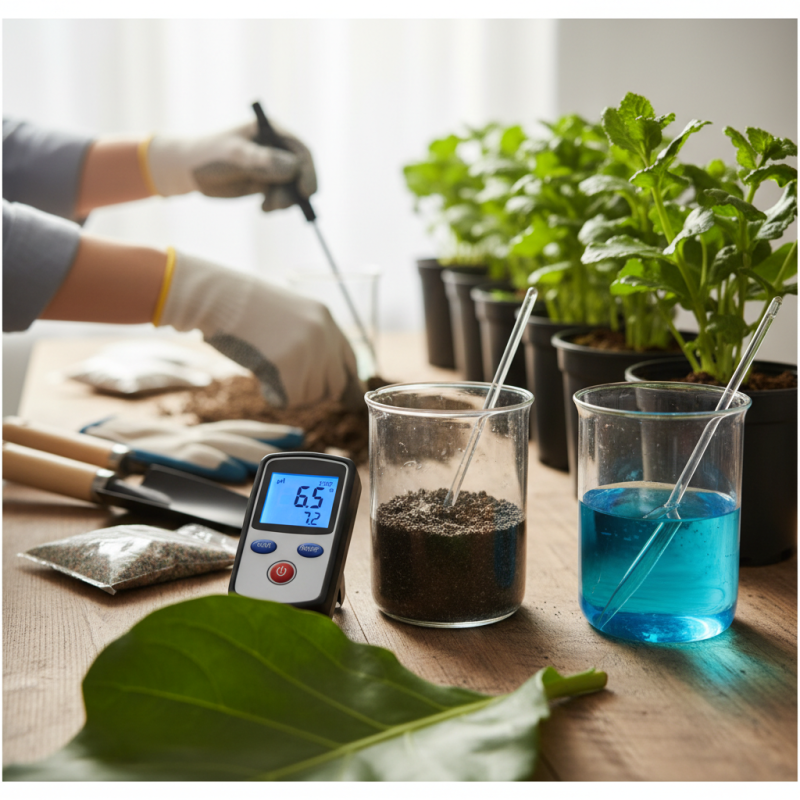

Importance of pH Testing in Soil and Water Analysis
pH testing is a crucial component of soil and water analysis, as it provides vital insights into the health and fertility of soil, as well as the quality of water sources. The pH level indicates whether a substance is acidic, neutral, or alkaline, which directly affects nutrient availability for plants and the biological processes in aquatic environments. For instance, most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6-7), while extreme pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, hampering growth and crop yields.
In water analysis, pH plays a significant role in assessing water quality for drinking, irrigation, and aquatic life. Variations in pH can impact various chemical reactions, including the solubility of minerals and metals, thus affecting the overall ecosystem. For aquatic environments, maintaining a balanced pH is essential to support diverse life forms, as many species are sensitive to changes in acidity or alkalinity. Therefore, regular pH testing of both soil and water is imperative for sustainable agriculture, environmental conservation, and ensuring safe and healthy ecosystems.
Choosing the Right pH Tester for Your Needs
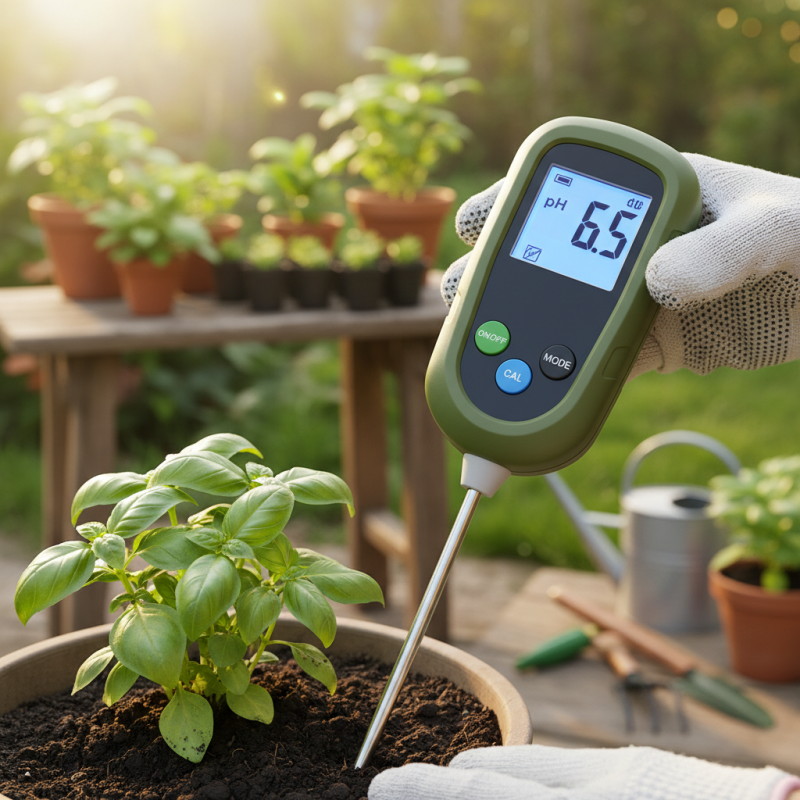

When choosing the right pH tester for your needs, it’s essential to consider the specific type of testing you plan to conduct, whether for soil, water, or both. For general gardening and small-scale horticulture, a handheld digital pH tester may be sufficient. These models are user-friendly, portable, and provide quick readings, making them ideal for amateur gardeners. However, it’s important to evaluate their accuracy, as lower-cost models may deliver inconsistent results over time.
For more advanced applications, such as agricultural research or professional landscaping, investing in a laboratory-grade pH meter can be beneficial. These devices often feature advanced calibration options and more sensitive probes, allowing for precise measurements. Additionally, consider durability and ease of maintenance; testers that come with replaceable batteries or probes can save time and costs in the long run. Always select a tester that suits your skill level and the intricacies of the tasks at hand to ensure accurate and reliable measurements.
Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Soil pH Levels
Measuring soil pH levels is crucial for understanding the nutrient availability and overall health of your garden or agricultural land. To begin, gather your materials: a pH tester, distilled water, a clean container, and a soil sample from the area you wish to test. It’s best to take samples from various spots to get an accurate representative measurement. Once you have your soil samples, remove any debris like stones or plant material to ensure a pure reading.
Next, prepare the soil sample by mixing a specific amount of soil with distilled water in your container. A common ratio is 1 part soil to 1 part water. Stir the mixture thoroughly until the soil is saturated and allows for even distribution. After letting it sit for about 15 minutes, insert your pH tester into the solution. Wait for the reading to stabilize and take note of the pH level displayed. This information will help you determine how to amend your soil for optimal plant growth, whether that means adding lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it.
How to Use a PH Tester for Accurate Soil and Water Testing - Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Soil pH Levels
| Sample Type | pH Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Garden Soil | 6.5 | Ideal for most plants |
| Potting Soil | 5.8 | Consider adding lime to raise pH |
| Lawn Soil | 7.0 | Maintain current pH for optimal grass growth |
| Water Sample | 7.2 | Safe for most aquatic life |
| Compost | 6.0 | Good for soil amendment |
Optimal pH Range for Common Plants and Crops
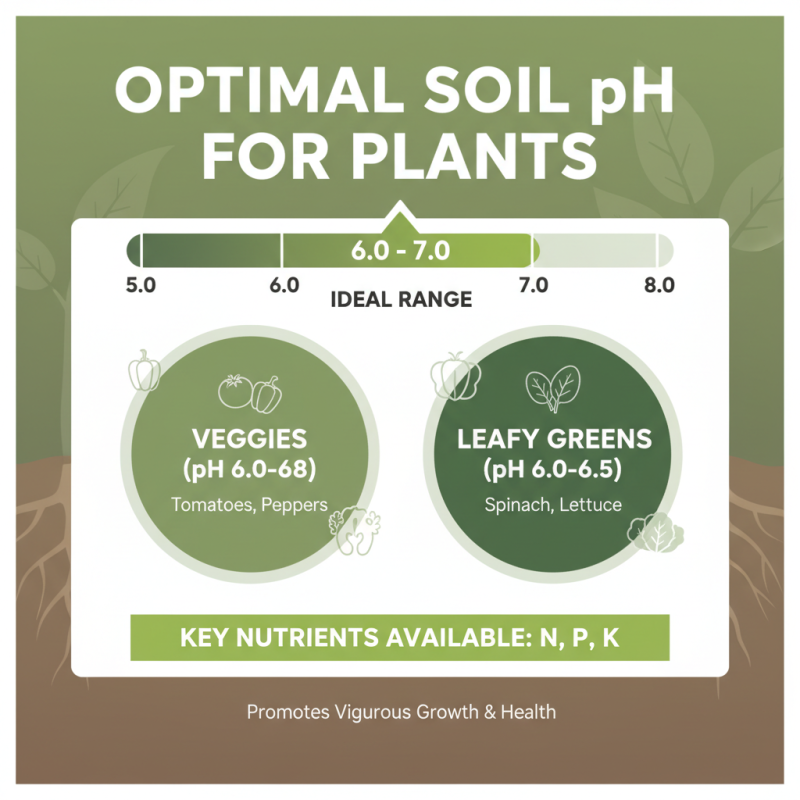
The optimal pH range is crucial for the growth of a variety of plants and crops, as it directly affects nutrient availability and overall plant health. Most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil, with an ideal pH range typically between 6.0 and 7.0. Within this range, essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium become more accessible to the roots, promoting vigorous growth and development. For instance, vegetables like tomatoes and peppers prefer a pH of around 6.0 to 6.8, while leafy greens such as spinach and lettuce are happiest in a slightly more acidic environment, ideally around 6.0 to 6.5.
Certain crops, however, have unique pH preferences that can significantly impact their yield and quality. For example, blueberries, which are acid-loving plants, thrive in a more acidic range of about 4.5 to 5.5, while asparagus can tolerate a slightly more alkaline environment with a preferred pH of 7.0 to 8.0. Understanding these specific pH requirements can help gardeners and farmers adjust their soil conditions accordingly, using amendments or natural fertilizers to create the perfect growing environment. By monitoring soil pH levels regularly, you can ensure that your plants receive the essential nutrients they need for optimal growth and productivity.
Interpreting pH Levels and Adjusting Soil Chemistry
Interpreting pH levels in soil and water is crucial for maintaining healthy plants and optimal growing conditions. A pH scale ranging from 0 to 14 indicates how acidic or alkaline a substance is, with 7 being neutral. Soil pH can significantly impact nutrient availability; for instance, a pH below 6.0 can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like nitrogen and potassium, while a pH above 7.0 may hinder the absorption of iron and manganese. Regularly testing soil and water pH can help gardeners and farmers make informed decisions about amendments and fertilizer applications.
Adjusting soil chemistry often involves amending the soil based on pH readings. If the soil is too acidic, adding lime can help raise the pH, making essential nutrients more accessible to plants. Conversely, if the soil is too alkaline, sulfur or organic matter can be incorporated to help lower the pH. It is essential to make these adjustments gradually and to retest pH levels after modifications to avoid over-correction, which can lead to additional nutrient imbalances. By understanding and managing pH levels, landowners can create an environment that promotes healthy plant growth and yields.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top PH Tester for Water Enhancing Quality and Safety with Accurate Measurements
-

Top 10 Tap Water Test Kits for Safe Drinking Water at Home
-

Why Is Drinking Water Test Essential for Your Health and Safety
-

2025 Top 5 Benefits of Chlorine Dioxide Water Treatment You Need to Know
-

Why You Should Use a Water Quality Test Kit for Safe Drinking Water
-

Understanding Chlorine Dioxide Formula: Uses, Benefits, and Safety Measures

