What is a Conductivity Meter and How Does It Work?
A conductivity meter is an essential tool in various fields, including water quality testing and chemical analysis. It measures the electrical conductivity of a liquid, indicating the concentration of ions present. Understanding how this instrument works can unlock insights into the properties of different solutions.
These meters operate based on a straightforward principle. When an electrical current passes through a liquid, its conductivity reflects how well it conducts electricity. Factors like temperature and ion concentration play significant roles in these measurements. The design typically includes two electrodes submerged in the liquid.
However, using a conductivity meter is not without challenges. Calibration is crucial for accurate readings. Inconsistent results can arise due to temperature variations or contamination. While these devices are often reliable, they require careful handling. This highlights the importance of understanding their functionality and limitations.
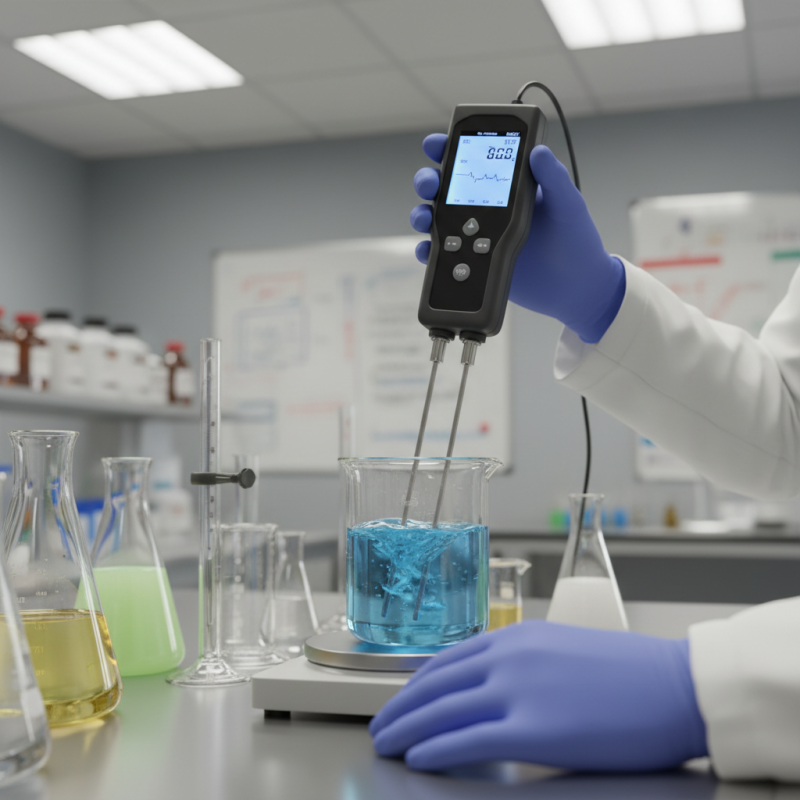

What is a Conductivity Meter? An Overview of Its Definition and Purpose
A conductivity meter is a tool used to measure the ability of a liquid to conduct electricity. This measurement is essential in various fields, including environmental monitoring and water quality testing. The conductivity of water can indicate the presence of dissolved salts and minerals. For many industries, understanding conductivity is crucial for maintaining product quality.
These meters work by passing an electric current through the liquid. The amount of current that flows depends on how many charged particles are present. More ions equal higher conductivity. This process is not without limitations. Factors like temperature can affect readings. If the water is too warm or cold, the results may be skewed.
Often, users must calibrate their meters for accuracy. Calibration can be a hassle. Many forget to do it regularly. Over time, the readings might become misleading. This highlights the importance of routine maintenance. A conductivity meter is a valuable tool, but it's not foolproof. Understanding its limitations is key for effective use.
The Principle of Conductivity Measurement: Understanding Ions and Conductivity
Conductivity meters measure the ability of water to conduct electricity. This capability is closely linked to the presence of ions. Ions are charged particles that derive from dissolved salts and minerals in a solution. The concentration of these ions significantly influences the conductivity level. Studies show that pure water has a very low conductivity. In contrast, seawater can have a conductivity of about 55,000 µS/cm due to its high ion concentration.
The measurement principle involves passing an electric current through the solution. A conductivity meter typically has two electrodes. When ions move towards the electrodes, they facilitate electron flow. This flow is measured, indicating the solution's conductivity level. Interestingly, at times, the results can mislead. Poor calibration of the meter can yield inaccurate readings. Additionally, temperature variations also impact conductivity. For every increase of 1°C, conductivity can increase by 2% to 3%. It's crucial to consider these factors for precise measurements in various industries.
Key Components of a Conductivity Meter: Sensors and Electronics Explained
A conductivity meter is a sophisticated device used to measure the electrical conductivity of liquids. Understanding its key components is crucial for its effective use. The primary part of a conductivity meter is the sensor. This sensor typically consists of two electrodes. These electrodes are submerged in the liquid to measure how well it conducts electricity.
When the electrodes are placed in a solution, an electric current flows between them. The meter calculates the conductivity based on this current. It's interesting to note that the material of the electrodes can affect the readings. Sometimes, users might overlook this factor. The wrong choice can lead to inaccurate measurements.
The electronics in the meter play a crucial role. They process the signals from the sensor and convert them into readable data. Many users may not fully appreciate the complexity of this process. Basic meters might struggle with varied solutions, leading to frustration. Regular calibration is essential. Inconsistent results can confuse, making understanding the meter's components vital for reliable usage.
Applications of Conductivity Meters in Water Quality and Industry Standards
Conductivity meters play a crucial role in monitoring water quality. They measure the electrical conductivity of water, which indicates the presence of ions. High conductivity levels can signal pollution or contamination. Many industries rely on these meters to ensure safe and clean water.
In municipal water systems, conductivity meters help detect impurities. These instruments guide treatment processes to remove contaminants. Additionally, in agricultural settings, they monitor irrigation water quality. Farmers need to know the salt concentration for healthy crops. In laboratories, conductivity measurements are essential for various experiments, ensuring accuracy in results.
However, not all conductivity meters are accurate. Calibration issues can lead to misleading readings. Users must regularly check their devices for reliability. Misuse can occur if users rely solely on these meters without understanding their limitations. Continuous education is necessary for effective water management practices across industries.
What is a Conductivity Meter and How Does It Work? - Applications of Conductivity Meters in Water Quality and Industry Standards
| Parameter | Unit | Typical Range for Drinking Water | Industrial Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | µS/cm | 50 - 500 | EPA < 1000 |
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | mg/L | 30 - 300 | FDA < 500 |
| Salinity | g/L | < 1 | ISO < 3 |
| pH Level | - | 6.5 - 8.5 | WHO 6.5 - 8.5 |
Interpreting Conductivity Readings: Units, Ranges, and Calibration Methods
Conductivity meters play a critical role in various fields, especially in environmental testing and water quality assessment. Understanding conductivity readings involves familiarizing oneself with units and ranges. Typically, conductivity is measured in microsiemens per centimeter (µS/cm). This unit reflects the water’s ability to conduct electrical current, which varies based on dissolved ions.
For practical applications, knowing the expected ranges for different water types is essential. Freshwater might range from 50 to 500 µS/cm, whereas seawater is much higher, around 30,000 µS/cm. Calibration methods often include using standard solutions. These solutions must be stable and properly stored to ensure accuracy. Inaccurate calibration can lead to misleading results, which can be critical in decision-making processes.
Regular checks on calibration solutions can sometimes be overlooked. A user may assume a meter is functioning well without validating its readings against a standard. This can lead to errors in sample analysis. It’s important to reflect on and test these assumptions periodically to maintain reliable readings and proper metrics.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Conductivity Meters for Accurate Water Quality Measurement
-

How to Choose the Best Home Water Test Kit for Safe Drinking Water
-
Best Tap Water Test Kits for Safe Drinking Water?
-

Top 10 Tap Water Test Kits for Safe Drinking Water at Home
-

Top 5 Best Ec Meters for Accurate Water Quality Testing?
-

Top Water Testing Tips for Homeowners to Ensure Safe Drinking Water

